Duolingo English Test: 10 Advanced Vocabulary for “Speaking Sample” - Ethics and Morality
Focused on Duolingo English Test preparation, this blog post offers ten advanced words related to ethics and morality. It provides definitions, usage examples, and practical tips, helping users articulate their thoughts on ethical dilemmas like lying and honesty, with a sample response discussing when lying might be morally acceptable.
| Speaking Sample | Technology and Internet |
|---|---|
| Personal Development and Growth | |
| Education and Learning | |
| Opinions and Beliefs | |
| Time and Life Management | |
| Relationships and Social Skills | |
| Hobbies and Interests | |
| Career and Work | |
| Cultural and Historical Topics | |
| Travel and Geography | |
| Health and Wellness | |
| Entertainment and Media | |
| Ethics and Morality | |
| Personal Experiences and Memories | |
| Society and Global Issues |
DET Advanced Vocabulary List and Applications
1. Benevolent
Definition: Kind and well-meaning; showing a desire to help others.
Example: A benevolent organization dedicates itself to supporting underprivileged communities.
Usage Tip: Use this term to describe individuals or organizations that prioritize altruism.
2. Justification
Definition: The action of demonstrating something to be right or reasonable; a reason for an action.
Example: The manager provided a clear justification for the company’s decision to cut costs.
Usage Tip: Discuss situations where ethical choices require solid justification.
3. Deception
Definition: The act of misleading someone through falsehoods.
Example: Deception in advertising can lead to a significant loss of consumer trust.
Usage Tip: Highlight the ethical implications of deception in various contexts.
4. Credibility
Definition: The quality of being trusted and believed; reliability.
Example: Maintaining credibility is essential for professionals across all fields.
Usage Tip: Discuss how credibility influences ethical decision-making and public perception.
5. Hypocrisy
Definition: The practice of claiming to have moral standards or beliefs that one’s own behavior does not conform to.
Example: The politician’s hypocrisy was evident when his actions contradicted his stated values.
Usage Tip: Use this term to critique inconsistencies between stated beliefs and actions.
6. Conscience
Definition: An inner sense of right and wrong that guides a person’s thoughts and actions.
Example: Her conscience urged her to speak out against the injustice she witnessed.
Usage Tip: Discuss how conscience influences ethical decisions in various scenarios.
7. Culpability
Definition: The degree to which a person is responsible for wrongdoing; guilt.
Example: Establishing culpability is crucial in legal cases involving ethical breaches.
Usage Tip: Use this term when discussing accountability for unethical behavior.
8. Accountability
Definition: The obligation to explain, justify, and take responsibility for one’s actions.
Example: Accountability in leadership fosters a culture of trust and integrity.
Usage Tip: Emphasize the importance of accountability in ethical practices.
9. Fidelity
Definition: Faithfulness to a person, cause, or belief; loyalty.
Example: Fidelity to ethical principles often guides professionals in their decision-making.
Usage Tip: Discuss how fidelity enhances trust in relationships and organizations.
10. Transparency
Definition: Openness and clarity in communication and actions; allowing others to see what is happening.
Example: Transparency in governance is vital for public trust and engagement.
Usage Tip: Highlight the role of transparency in promoting ethical behavior.
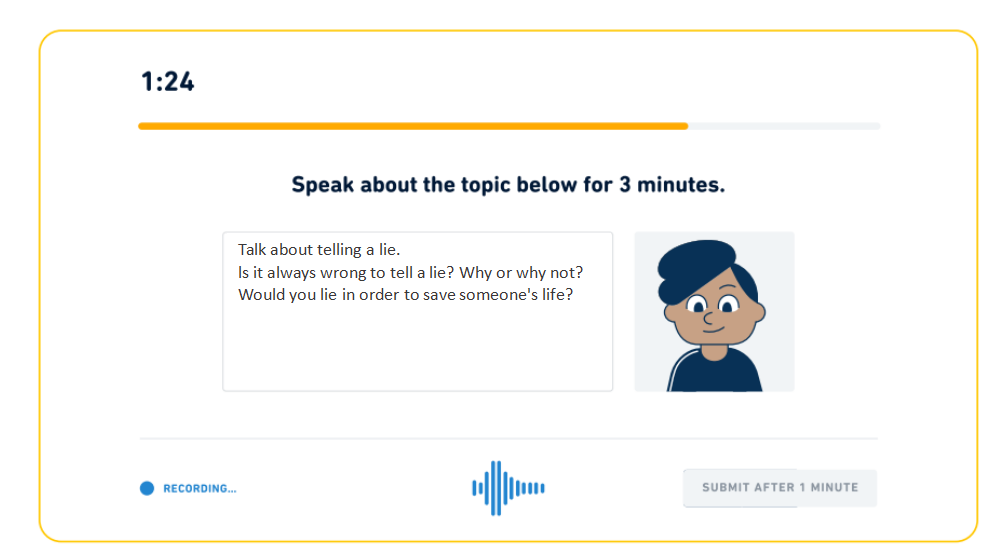
Sample Answer:
In my opinion, telling a lie is often a complex ethical issue. While deception is generally viewed as wrong, there are situations where it may be justified. For instance, if a lie can protect someone from harm or even save a life, it raises important questions about accountability and culpability. In such cases, the justification for lying could stem from a benevolent intention to help others. However, one must also consider the potential consequences of the lie. If a lie undermines trust, it can lead to hypocrisy, where one’s actions contradict their stated values and beliefs. Therefore, while I firmly believe that honesty is crucial in most situations, there are rare instances where a lie might be ethically permissible, especially when it serves the greater good and protects those in need. In these cases, the moral implications should be carefully weighed to ensure the best outcome for everyone involved.
Further Reading:
l DET Prep Course: Speaking Sample Questions
(An article about a comprehensive course and exercises on Speaking Samples.)
l 10 Advanced Vocabulary for “Writing Sample” in the Duolingo English Test - Personal Experience
(An article about advanced vocabulary for Writing Samples.)
l Duolingo English Test: 10 Advanced Vocabulary for “Speaking Sample” - Entertainment and Media
(An article about advanced vocabulary for Speaking Samples.)